Vinz
C# Language Tips 3
 Մι∩z•thedev · Follow
Published in Coding · 6 min read · 1 day ago
__
👏65k 💬321 🔖 ⤴️
__
Մι∩z•thedev · Follow
Published in Coding · 6 min read · 1 day ago
__
👏65k 💬321 🔖 ⤴️
__
Here are the fishes I angled while coding. You can fry them the way you like, just share with the community, ie. Stackoverflow is my favorite ;-)
Foreword ‘EF’ for non-initiated ones is diminutive for ‘Entity Framework’, the reference ORM for .Net
primary constructors
less typing, very convenient for dependency injection
public class MyService
{
private readonly IRepository _repo;
public MyService(IRepository repo)
{
_repo = repo;
}
}
//turns into
public class MyService(IRepository repo)
{
}
EF without state management
By default EF tracks all the changes, for good (what do you expect of an ORM after all?) and for worse (performance…) Some design are simply not compatible with EF default behavior, hence needing to tune it to be much more like a query builder than a full-fledged ORM.
//find+detach
var thing = _dbContext.Things.Find(thingId);
_dbContext.Entry<TThing>(thing).State = EntityState.Detached;
//add+detach
var entity = _dbContext.Add(thing)
_dbContext.SaveChanges();
entity.State = EntityState.Detached;
//query+detached
public IQueryable<TThing> Things
=> _dbContext.Things.AsNoTracking();
EF Exceptions
//enable meaningful EF exception message, don't! if sensitive...
public class MyContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder builder)
{
builder.EnableSensitiveDataLogging();
}
}
Transactions
//1.newer TransactionScope
using var scope = new TransactionScope()
...
scope.Complete();
//--vs--
//2.older BeginTransaction
using var transaction = _back.Database.BeginTransaction();
...
transaction.Commit()
/*or*/ transaction.Rollback();
// TransactionScope is auto rollback on fail
try
{
using var transactionScope = new TransactionScope();
// if success so far, commit the transaction
transactionScope.Complete();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// transaction will be rolled back if exception occurs
}
// TransactionScope does async
using var scope = new TransactionScope(
TransactionScopeAsyncFlowOption.Enabled)
await context.Things.ToListAsync().ConfigureAwait(false);
// TransactionScope allows easier nested scope in scope
//BUT TransactionScope not supported by all db, ie. sqlite,
// so BeginTransaction is more reliable
Parsable
That’s for .NET Core API to be able to parse nullable int, which is not as trivial as it seems
booking.MapGet("/", (
...
[FromQuery(Name = "pricemin")] NullableInt priceMin,
[FromQuery(Name = "pricemax")] NullableInt priceMax,
...
)
=> ...
public class NullableInt : IParsable<NullableInt>
{
public int? Value { get; init; } = null;
public static NullableInt Parse(string value, IFormatProvider? provider)
{
if (!TryParse(value, provider, out var result))
{
throw new ArgumentException("Could not parse supplied value.", nameof(value));
}
return result;
}
public static bool TryParse(string? value, IFormatProvider? provider, out NullableInt nullableInt)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value))
{
nullableInt = new NullableInt();
return true;
}
if (int.TryParse(value, out var intValue))
{
nullableInt = new NullableInt() { Value = intValue };
return true;
}
nullableInt = new NullableInt();
return false;
}
}
Producer loop : yield
yield return, yield break, yield continue, same as traditional return, break, continue but operates as IEnumerable. That’s interesting because the data is produced just-in-time and not in bulk, hence preserving resources and reducing latency.
public IEnumerable<Item> GetItems()
{
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
yield return new Item
{
Id = i
};
}
}
Funny C#8+ indexers
var numbers = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
//C#8+ indexers
numbers[0] // first element <--> numbers[length-length]
numbers[4] // last element <--> numbers[length-1]
numbers[^5] // first element <--> numbers[length-length]
numbers[^1] // last element <--> numbers[length-1]
numbers[2..^3];
numbers[..^3]; //<--> numbers[0..^3];
numbers[2..];//<--> numbers[2..^0];
numbers[..];//<--> numbers[0..^0];
string str = "/a/b/c/"
str[..^1] //trim end slash
str[^1..] //trim start slash
Range indexes = 0..4;
int[] numbers = [..Enumerable.Range(0, 5)];
Span<int> subnumbers = numbers[1..3];
//funny but not always very useful
Range to replace for loop
for(int i = start; i < count; i++) ...
//changed for
Enumerable
.Range(start, count)
.ForEach(i => ...
For example, let’s convert a string of hex characters to bytes (we need 2 hex digits to make up 1 byte and repeat…)
ret = Enumerable
.Range(0, hex.Length)
.Where(i => i % 2 == 0)
.Select(i => Convert.ToByte(hex.Substring(i, 2), 16))
.ToArray();
To be or not to be Nullable…
Thing is nullable int is not nullable int? is nullable …
public static bool IsNullable(this Type ClrType)
{
if(!ClrType.IsValueType)
return true; // Reference Type
if (Nullable.GetUnderlyingType(ClrType) != null)
return true; // Nullable<T>
return false; // Value Type
}
Underlying type
public static Type GetUnderlyingClrType(this Type ClrType)
{
get
{
if (ClrType == typeof(string))
{
return ClrType;
}
if (!IsNullable(ClrType))
{
return ClrType;
}
return Nullable.GetUnderlyingType(ClrType);
}
}
Range enumeration
You like range from, count ? You want range from, to ?
public static class EnumerableHelper
{
public static IEnumerable<int> RangeTo(this int from, int to)
{
return Enumerable.Range(from, to - from + 1);
}
Random order enumeration
public static class EnumerableHelper
{
private static Random Random = new Random();
public static IEnumerable<T> AsRandomEnumerable<T>(this IEnumerable<T> collection)
{
var scrambled = collection
.OrderBy(item => Random.Next());
foreach (var item in scrambled)
{
yield return item;
}
}
Hash-32 not enough
Sometimes you feel you should extend the yard were you throw peebles into, to avoid possible wreck… that does not mean you shouldn’t double-check collisions….
Here is a way to get Hash-64 for a string
public static class HashHelper
{
private static BlockingCollection<SHA256> Shas = NewShaCollection();
private static BlockingCollection<SHA256> NewShaCollection()
{
var ret = new BlockingCollection<SHA256>(Environment.ProcessorCount);
for (var i = 0; i < ret.BoundedCapacity; i++)
{
ret.Add(SHA256.Create());
}
return ret;
}
private static T? GetASha<T>(Func<SHA256, T?> use)
{
var sha = Shas.Take();
Exception? ex = default;
T ret = default;
try
{
ret = use(sha);
}
catch (Exception ex_)
{
ex = ex_;
}
Shas.Add(sha);
if (ex != null)
{
throw ex;
}
return ret;
}
public static long GetHashCode64(this string str)
{
var bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(str);
return GetHashCode64(bytes);
}
public static long GetHashCode64(params byte[][] byteArrays)
=> GetHashCode64(byteArrays
.Select(arr => arr.AsEnumerable())
.Aggregate((arr1, arr2) => arr1.Concat(arr2))
.ToArray());
public static long GetHashCode64(this IEnumerable<byte> bytes)
=> GetHashCode64(bytes.ToArray());
public static long GetHashCode64(this byte[] bytes) => GetASha(aSha =>
{
var sha = aSha.ComputeHash(bytes); //32 bytes
ulong uhash = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
var b = sha[i * 8 + j];
uhash ^= (ulong)b << j * 8;
}
}
var hash = unchecked((long)uhash + long.MinValue);
return hash;
});
}
DateTime rounded to the second
private static readonly long HalfSecondTicks = TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond / 2;
public static DateTime RoundToTheSecond(this DateTime date)
{
var ret = date;
var fractionalTicks = ret.Ticks % TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond;
ret = ret.AddTicks(-fractionalTicks);
if (fractionalTicks >= HalfSecondTicks)
{
ret = ret.AddTicks(TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond);
}
return ret;
}
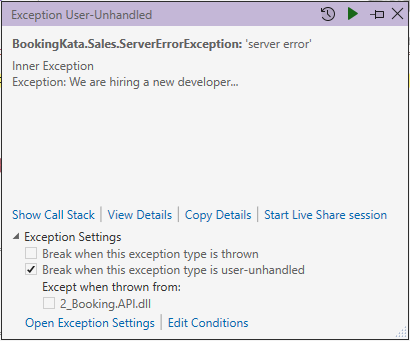
Lost in Translation
EF, do you copy that ?
//query the IQueryable
if (query.LostInTranslation(out var sql, out var translationError))
{
throw new ServerErrorException(new Exception("We are hiring a new developer..."));
}
public static bool LostInTranslation<TEntity>
(
this IQueryable<TEntity> query,
out string? sql,
out string? translationError
)
where TEntity : class
{
try
{
sql = query.ToQueryString();
translationError = null;
return false;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
sql = null;
translationError = ex.Message;
Console.Error.WriteLine($@"Lost in translation!
{translationError}");
return true;
}
}
Program information
//That helper parse and print Program name, version and build configuration
// ie. Booking.API.exe 1.24.3.29 (Debug)
//tested in windows
//not tested in mac, linux, please improve
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
namespace VinZ.ToolBox;
public record ProgramInfo(string? ExeName, string ExeVersion, string BuildConfiguration)
{
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine(@$"
{ExeName} {ExeVersion} ({BuildConfiguration})
");
}
public static ProgramInfo Current
=> GetProgramInfo(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly());
public static ProgramInfo GetProgramInfo(Assembly assembly)
{
var dllPath = assembly.Location;
var rx = new Regex(@"^(?<path>.*)\.dll$");
var match = rx.Match(dllPath);
var exePath = !match.Success ? default : match.Result("${path}.exe");
var exeName = exePath == default ? default : Path.GetFileName(exePath);
var exeVersion = exePath == default ? "???" : System.Diagnostics.FileVersionInfo.GetVersionInfo(exePath).FileVersion;
var buildConfiguration = IsDebugBuild(assembly) ? "Debug" : "Release";
return new ProgramInfo(exeName, exeVersion, buildConfiguration);
}
public static bool IsDebugBuild(Assembly assembly)
{
return assembly
.GetCustomAttributes(false)
.OfType<DebuggableAttribute>()
.Any(attr => attr.IsJITTrackingEnabled);
}
}
discard assignment
_ = who_the_hells_cares_about;
_ = 2024; //roughly means, let's forget 2024 ...
//much more useful is tuple partial deconstruction
var (_, fun, _) = tuple; //do your shopping !
switch regex
var str = "yummy";
switch (str)
{
case var s when Regex.IsMatch(s, "yucky"):
something = 1;
break;
case var s when Regex.IsMatch(userName, "yummy"):
something = 2;
break;
default:
break;
}